What is CSS?
Cascading Style Sheets, fondly referred to as CSS, is a simple design language intended to simplify the process of making web pages presentable.
CSS handles the look and feel part of a web page. Using CSS, you can control the color of the text, the style of fonts, the spacing between paragraphs, how columns are sized and laid out, what background images or colors are used, as well as a variety of other effects.
CSS is easy to learn and understand but it provides a powerful control over the presentation of an HTML document. Most commonly, CSS is combined with the markup languages HTML or XHTML.
Advantages of CSS?
- CSS saves time - You can write CSS once and then reuse the same sheet in multiple HTML pages. You can define a style for each HTML element and apply it to as many web pages as you want.
- Pages load faster - If you are using CSS, you do not need to write HTML tag attributes every time. Just write one CSS rule of a tag and apply it to all the occurrences of that tag. So, less code means faster download times.
- Easy maintenance - To make a global change, simply change the style, and all the elements in all the web pages will be updated automatically.
- Multiple Device Compatibility - Style sheets allow content to be optimized for more than one type of device. By using the same HTML document, different versions of a website can be presented for handheld devices such as PDAs and cellphones or for printing.
- Global web standards – Now HTML attributes are being deprecated and it is being recommended to use CSS. So it’s a good idea to start using CSS in all the HTML pages to make them compatible with future browsers.
Why Use CSS?
CSS is used to define styles for your web pages, including the design, layout and variations in display for different devices and screen sizes.
CSS Solved a Big Problem
HTML was NEVER intended to contain tags for formatting a web page!
HTML was created to describe the content of a web page, like:
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
When tags like <font>, and color attributes were added to the HTML 3.2 specification, it started a nightmare for web developers. Development of large websites, where fonts and color information were added to every single page, became a long and expensive process.
To solve this problem, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) created CSS.
CSS removed the style formatting from the HTML page!
Who Creates and Maintains CSS?
CSS is created and maintained through a group of people within the W3C called the CSS Working Group. The CSS Working Group creates documents called specifications. When a specification has been discussed and officially ratified by the W3C members, it becomes a recommendation.
These ratified specifications are called recommendations because the W3C has no control over the actual implementation of the language. Independent companies and organizations create that software.
NOTE − The World Wide Web Consortium, or W3C is a group that makes recommendations about how the Internet works and how it should evolve.
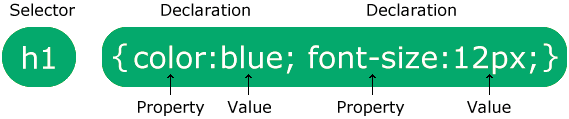
Selector: Selector indicates the HTML element you want to style. It could be any tag like <h1>, <title> etc.
Declaration Block: The declaration block can contain one or more declarations separated by a semicolon. For the above example, there are two declarations:
- color: yellow;
- font-size: 11 px;
Each declaration contains a property name and value, separated by a colon.
Property: A Property is a type of attribute of HTML element. It could be color, border etc.
Value: Values are assigned to CSS properties. In the above example, value "yellow" is assigned to color property.
Example:
Out Put:
Example Explained
pis a selector in CSS (it points to the HTML element you want to style: <p>).coloris a property, andredis the property valuetext-alignis a property, andcenteris the property value
CSS Selectors
CSS selectors are used to select the content you want to style. Selectors are the part of CSS rule set. CSS selectors select HTML elements according to its id, class, type, attribute etc.
There are several different types of selectors in CSS.
- CSS Element Selector
- CSS Id Selector
- CSS Class Selector
- CSS Universal Selector
- CSS Group Selector
1.The CSS element Selector
The element selector selects HTML elements based on the element name.
Example:
Out Put:
2.The CSS id Selector
The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element.
The id of an element is unique within a page, so the id selector is used to select one unique element!
To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character, followed by the id of the element.
Let?s take an example with the id "para1".
Example:
Out Put:
3.The CSS class Selector
The class selector selects HTML elements with a specific class attribute.
To select elements with a specific class, write a period (.) character, followed by the class name.
Let's take an example with a class "center".
Example:
Out Put:
4.The CSS Universal Selector
The universal selector (*) selects all HTML elements on the page.The universal selector is used as a wildcard character.
Example:
Out Put:
5.The CSS Grouping Selector
The grouping selector selects all the HTML elements with the same style definitions.
Look at the following CSS code (the h1, h2, and p elements have the same style definitions):
To group selectors, separate each selector with a comma.
Example:
All CSS Simple Selectors
| Selector | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| #id | #firstname | Selects the element with id="firstname" |
| .class | .intro | Selects all elements with class="intro" |
| element.class | p.intro | Selects only <p> elements with class= "intro" |
| * _ | * | Selects all elements |
| element | p | Selects all <p> elements |
| element,element,.. | div, p | Selects all <div> elements and all <p> elements |
How To Add CSS
When a browser reads a style sheet, it will format the HTML document according to the information in the style sheet.
Three Ways to Insert CSS
here are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
- External CSS
- Internal CSS
- Inline CSS
External CSS
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the <link> element, inside the head section.
Example
External styles are defined within the <link> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page.
The external .css file should not contain any HTML tags.
Internal CSS
An internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style.
The internal style is defined inside the <style> element, inside the head section.
Example
Internal styles are defined within the <style> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page:
Out Put:
Inline CSS
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
To use inline styles, add the style attribute to the relevant element. The style attribute can contain any CSS property.
Example
Inline styles are defined within the "style" attribute of the relevant element:
Cascading Order
What style will be used when there is more than one style specified for an HTML element?
All the styles in a page will "cascade" into a new "virtual" style sheet by the following rules, where number one has the highest priority:
- Inline style (inside an HTML element)
- External and internal style sheets (in the head section)
- Browser default
So, an inline style has the highest priority, and will override external and internal styles and browser defaults.
Example:
Out Put:
CSS Comments
Comments are used to explain the code, and may help when you edit the source code at a later date.
Comments are ignored by browsers.
A CSS comment is placed inside the <style> element, and starts with /* and ends with */
Example:
CSS Backgrounds
- background-color
- background-image
- background-repeat
- background-attachment
- background-position
CSS background-color
background-color property specifies the background color of an element.With CSS, a color is most often specified by:
- a valid color name - like "red"
- a HEX value - like "#0000FF"
- an RGB value - like "rgb(0,0,255)"
Can you set the background color for any HTML elements:
Example:
CSS background-image
background-image property specifies an image to use as the background of an element. By default, the image is repeated so it covers the entire element.Example:
The background image can also be set for specific elements, like the <p> element:
Example:
CSS background-repeat
background-image property repeats an image both horizontally and vertically.If the image above is repeated only horizontally (
background-repeat: repeat-x;), the background will look better:CSS background-attachment
Thebackground-attachment property specifies whether the background image should scroll or be fixed .If you set fixed the background image then the image will not move during scrolling in the browser.CSS background-position
background-position property is used to specify the position of the background image.CSS Borders
The CSS border properties allow you to specify the style, width, and color of an element's border.CSS Border Style
The border-style property specifies what kind of border to display.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| none | It doesn't define any border. |
| dotted | It is used to define a dotted border. |
| dashed | It is used to define a dashed border. |
| solid | It is used to define a solid border. |
| double | It defines two borders wIth the same border-width value. |
| groove | It defines a 3d grooved border. effect is generated according to border-color value. |
| ridge | It defines a 3d ridged border. effect is generated according to border-color value. |
| inset | It defines a 3d inset border. effect is generated according to border-color value. |
| outset | It defines a 3d outset border. effect is generated according to border-color value. |
The border-style property can have from one to four values (for the top border, right border, bottom border, and the left border).
Example:
CSS Border Width
border-width property is used to set the border's width.CSS Border Color
The border-color property is used to set the color of the four borders.
The color can be set by:
- name - specify a color name, like "blue"
- HEX - specify a HEX value, like "#0000FF"
- RGB - specify a RGB value, like "rgb(0,0, 255)"
- HSL - specify a HSL value, like "hsl(240, 100%, 50%)"
border-color is not set, it inherits the color of the element.This CSS property sets the rounded borders and provides the rounded corners around an element, tags, or div. It defines the radius of the corners of an element.
It is shorthand for border top-left-radius, border-top-right-radius, border-bottom-right-radius and border-bottom-left-radius.
This CSS property includes the properties that are tabulated as follows:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| border-top-left-radius | It is used to set the border-radius for the top-left corner |
| border-top-right-radius | It is used to set the border-radius for the top-right corner |
| border-bottom-right-radius | It is used to set the border-radius for the bottom-right corner |
| border-bottom-left-radius | It is used to set the border-radius for the bottom-left corner |
Example:
Example:
CSS Border-spacing
This CSS property is used to set the distance between the borders of the adjacent cells in the table. It applies only when the border-collapse property is set to separate. There will not be any space between the borders if the border-collapse.
It can be defined as one or two values for determining the vertical and horizontal spacing.
- When only one value is specified, then it sets both horizontal and vertical spacing.
- When we use the two-value syntax, then the first one is used to set the horizontal spacing (i.e., the space between the adjacent columns), and the second value sets the vertical spacing.
CSS Margins
The CSS margin properties are used to create space around elements, outside of any defined borders.
Top, bottom, left and right margin can be changed independently using separate properties. You can also change all properties at once by using shorthand margin property.
Example:
CSS has properties for specifying the margin for each side of an element:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| margin | This property is used to set all the properties in one declaration. |
| margin-left | it is used to set left margin of an element. |
| margin-right | It is used to set right margin of an element. |
| margin-top | It is used to set top margin of an element. |
| margin-bottom | It is used to set bottom margin of an element. |
CSS margin values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| auto | This is used to let the browser calculate a margin. |
| length | It is used to specify a margin pt, px, cm, etc. its default value is 0px. |
| % | It is used to define a margin in percent of the width of containing element. |
| inherit | It is used to inherit margin from parent element. |
Margin - Shorthand Property
- margin: 20px 40px 60px 80px;
- top margin is 20px
- right margin is 40px
- bottom margin is 60px
- left margin is 80px
margin property has three values:- margin: 20px 40px 60px;
- top margin is 20px
- right and left margins are 40px
- bottom margin is 60px
If the margin property has two values:
- margin: 20px 40px;
- top and bottom margins are 20px
- right and left margins are 40px
The inherit Value
The auto Value
auto to horizontally center the element within its container.CSS Margin Collapse
CSS Colors
CSS Background Color
CSS Border Color
CSS RGB Colors
Each parameter (red, green, and blue) defines the intensity of the color between 0 and 255.
For example, rgb(255, 0, 0) is displayed as red, because red is set to its highest value (255) and the others are set to 0.
To display black, set all color parameters to 0, like this: rgb(0, 0, 0).
To display white, set all color parameters to 255, like this: rgb(255, 255, 255).
Example:
CSS RGBA Colors
It is almost similar to RGB format except that RGBA contains A (Alpha) that specifies the element's transparency.
An RGBA color value is specified with:
rgba(red, green, blue, alpha)
The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (not transparent at all).
Example:
CSS HEX Colors
HEX Value
#rrggbb
Where rr (red), gg (green) and bb (blue) are hexadecimal values between 00 and ff (same as decimal 0-255).
To display black, set all values to 00, like this: #000000.
To display white, set all values to ff, like this: #ffffff.
Example:
3 Digit HEX Value
CSS HSL Colors
hsl(hue, saturation, lightness)
Hue is a degree on the color wheel from 0 to 360. 0 is red, 120 is green, and 240 is blue.
Saturation is a percentage value, 0% means a shade of gray, and 100% is the full color.
Lightness is also a percentage, 0% is black, 50% is neither light or dark, 100% is white.
Example:
Saturation
Saturation can be described as the intensity of a color.
100% is pure color, no shades of gray
50% is 50% gray, but you can still see the color.
0% is completely gray, you can no longer see the color.
Example:
Lightness
The lightness of a color can be described as how much light you want to give the color, where 0% means no light (black), 50% means 50% light (neither dark nor light) 100% means full lightness (white).
Example:
CSS HSLA Colors
An HSLA color value is specified with:
hsla(hue, saturation, lightness, alpha)
The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (not transparent at all).
Example:
CSS Padding
padding properties are used to generate space around an element's content, inside of any defined borders.| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| padding | It is used to set all the padding properties in one declaration. |
| padding-left | It is used to set left padding of an element. |
| padding-right | It is used to set right padding of an element. |
| padding-top | It is used to set top padding of an element. |
| padding-bottom | It is used to set bottom padding of an element. |
CSS Padding Values
All the padding properties can have the following values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| length | It is used to define fixed padding in pt, px, em etc. |
| % | It defines padding in % of containing element. |
Note: Negative values are not allowed.
Example:
Padding and Element Width
width property specifies the width of the element's content area. The content area is the portion inside the padding, border, and margin of an element .CSS Fonts
These are some important font attributes:
- CSS Font size: This property is used to increase or decrease the size of the font.
- CSS Font family: This property is used to change the face of the font.
- CSS Font color: This property is used to change the color of the text. (standalone attribute)
- CSS Font style: This property is used to make the font bold, italic or oblique.
- CSS Font variant: This property creates a small-caps effect.
- CSS Font weight: This property is used to increase or decrease the boldness and lightness of the font.
CSS Font size
font-size property sets the size of the text. Being able to manage the text size is important in web design. Absolute size:
- Sets the text to a specified size
- Does not allow a user to change the text size in all browsers (bad for accessibility reasons)
- Absolute size is useful when the physical size of the output is known
Relative size:
- Sets the size relative to surrounding elements
- Allows a user to change the text size in browsers
Font Size With Pixels
CSS Font family
There are two types of font-family names in CSS:
- family-name: It is the name of the font-family such as "Courier", "Arial", "Times", etc.
- generic-family: It is the name of the generic family that includes five categories, which are "serif", "sans-serif", "cursive", "fantasy", and "monospace". It should be placed at last in the list of the font family names.
Let's define the generic-family categories.
In CSS there are five generic font families:
- Serif fonts have a small stroke at the edges of each letter. They create a sense of formality and elegance.
- Sans-serif fonts have clean lines (no small strokes attached). They create a modern and minimalistic look.
- Monospace fonts - here all the letters have the same fixed width. They create a mechanical look.
- Cursive fonts imitate human handwriting.
- Fantasy fonts are decorative/playful fonts.
CSS Font color
There are three different formats to define a color:
- By a color name
- By hexadecimal value
- By RGB
Example:
CSS Font style
font-style property defines what type of font you want to display.This property has three values:
- normal - The text is shown normally
- italic - The text is shown in italics
- oblique - The text is "leaning" (oblique is very similar to italic, but less supported)
Example:
CSS Font variant
font-variant property specifies whether or not a text should be displayed in a small-caps font.CSS Text
CSS Text color
The color property is used to set the color of the text. The color is specified by:
- a color name - like "blue"
- a HEX value - like "#0000ff"
- an RGB value - like "rgb(0,0,255)"
Example:
Text Color and Background Color
background-color property and the color property:CSS Height and Width
The CSS height and width properties are used to set the height and width of an element.
The height and width properties do not include padding, borders, or margins. It sets the height/width of the area inside the padding, border, and margin of the element.
CSS height and width Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| auto | It is a default value. The browser calculates the height and width. |
| length | It specifies the height/width of an element using the length units such as px, cm, pt, etc. |
| % | It defines the height/width in percent(%) of the containing block. |
| initial | It is used to set the property to its default value. |
| inherit | It is used to inherit the property from its parent element. |
Example:













































































No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, Please let me know